Understanding Hives: How Long Do They Typically Last?
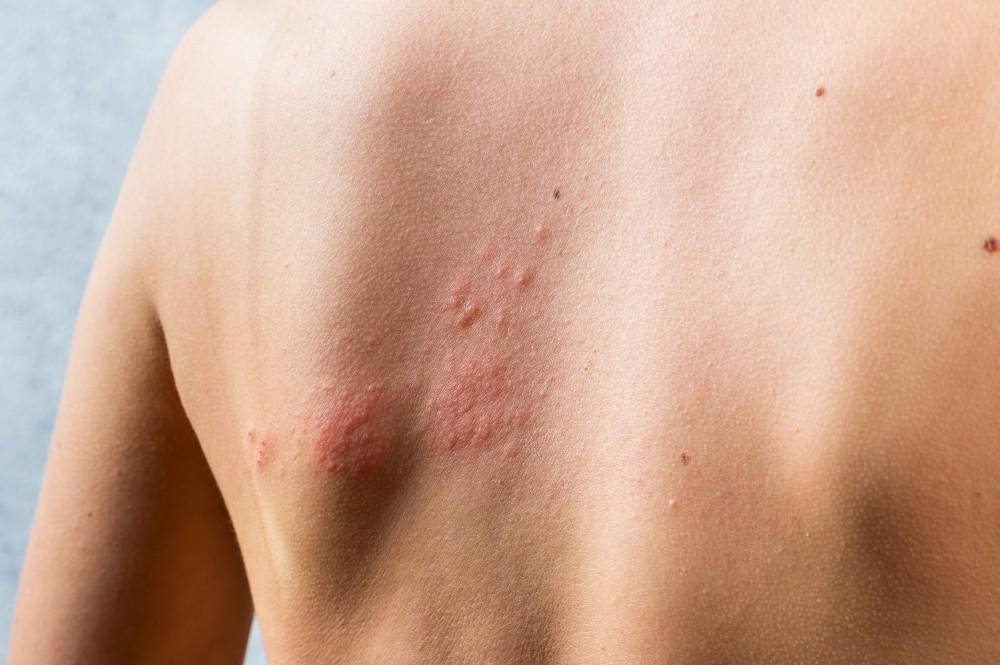
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts that can appear on the skin and vary in size and shape. They are a common skin reaction that can be triggered by various factors, including allergies, stress, medications, and infections. If you’ve experienced hives and are wondering how long do hives last, it’s important to understand that the duration can vary from person to person and depend on the underlying cause. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Acute Hives:
Acute hives are hives that last for a short period, typically less than six weeks. They often occur suddenly and are often related to an allergic reaction, such as to certain foods, medications, insect stings, or latex. Acute hives can be intensely itchy and uncomfortable but tend to resolve on their own within a few hours to a few days. In some cases, they may persist for several weeks but usually resolve within the acute timeframe.
2. Chronic Hives:
Chronic hives are hives that persist for six weeks or longer. They can be more challenging to manage and may require ongoing treatment. Chronic hives may not always have an identifiable trigger, making it more difficult to determine their cause. Stress, autoimmune conditions, and underlying health issues can contribute to chronic hives.
3. Factors Influencing Hives Duration:
The duration of hives can be influenced by several factors, including:
Underlying Cause: The specific trigger of the hives can affect how long they last. If the cause is identified and removed or treated, the hives are more likely to resolve sooner.
Treatment: Treatment options, such as antihistamines (which reduce itching and inflammation), can help alleviate symptoms and speed up the resolution of hives.
Individual Response: People react differently to hives, and some may experience hives more frequently or for longer durations than others.
Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can exacerbate hives or prolong their duration. Managing stress can be beneficial in reducing hives.
4. Seeking Medical Attention:
If you experience hives that last longer than a few days or are accompanied by severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or a sudden drop in blood pressure, seek immediate medical attention, as these can be signs of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
5. Treatment and Management:
For acute hives, over-the-counter antihistamines are often effective in reducing symptoms and hastening their resolution. However, for chronic hives, a healthcare provider may recommend a combination of antihistamines and other medications, such as corticosteroids or immune modulators, to manage symptoms and address underlying causes.
6. Prevention:
If you have a known trigger for hives, the best way to prevent them is to avoid the trigger. This may involve dietary changes, avoiding specific medications, or taking steps to reduce stress.
In summary, the duration of hives can vary, with acute hives typically lasting less than six weeks and chronic hives persisting for six weeks or longer. Timely identification of the trigger and appropriate treatment can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of hives. If you experience persistent or severe hives, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.


