What Distinguishes Acute Back Pain From Chronic Back Pain?
Even though back pain is a common issue, managing it is still tricky. Most people have either acute or persistent back pain. Acute back pain is joint and usually goes away in a few days, though in some cases, it can linger up to six weeks. Learn more about back pain by appointment with a back pain specialists.
The causes of acute back pain
Tendons, ligaments, and muscles that comprise the back’s soft tissues are frequently injured or strained, resulting in acute back pain. This is particularly valid when lifting a big object while hunching over. Back pain is a possible side effect if you have muscular spasms.
The causes of chronic back pain
Numerous illnesses can result in persistent back pain, such as:
- Disc degeneration
- aging-related degenerative arthritis
- Regularly experiencing herniated discs
- fractures caused by compression
- fibromyalgia, as well as additional chronic pain disorders.
It is recognizing the distinction between acute and persistent back pain. It has to do with how long something has been hurting and why. Acute pain typically starts suddenly and is brought on by a particular event, like an injury. Usually lasting no more than six weeks, acute pain disappears once the underlying cause is removed.
The duration is the main factor that separates these two categories of pain. Because your body heals from acute pain, your agony eventually passes.
- Bruises, cuts, or burns
- Strains and sprains
- fractures of the bones
- Operation
How can back pain, both acute and chronic, be treated?
Lotions, ointments, and anti-inflammatory and pain medications can all help reduce pain, though many are not meant to be used over an extended period. Medication-free treatments are usually better because they don’t require a prescription and can be used forever to enhance the quality of life.
Treatment options for acute back pain
Most of the time, mild acute back pain goes away. The patient should only be bedridden for a few days because extended bed rest can have adverse effects. Instead, to help you move more comfortably, the doctor might advise taking painkillers.
A back pain treatment may also suggest strengthening exercises to increase the strength of weak muscles and stretching exercises to release tight muscles.
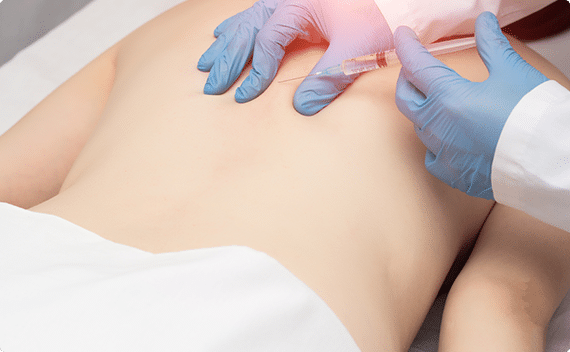
Chronic back pain treatment options
Since they can lead to physical dependence and tolerance, oral pain relievers are typically not intended for long-term use. For the management of chronic back pain, a mix of the following treatments can be employed:
- Injections used to treat pain
- Physiotherapy or physical therapy
- Injections of trigger points
- Treatment with medicine or surgery depending on a precise diagnosis
Conclusion
Acute back pain can survive anywhere from a few days to several weeks. With self-care, it usually goes away on its own in a few days, with no permanent function loss. Discomfort that stays for 12 weeks or more after therapy for an initial harm or underlying cause of back pain is called chronic back pain.
Both the terms “chronic” and “acute” are frequently misused when referring to back pain. It can be challenging to differentiate between acute and chronic pain, as well as whether untreated acute pain has the potential to develop into chronic pain. Consult a back doctor nj at a back center if your back pain interferes with your everyday routine.


