Thyroid Imbalance: Key Impacts on Physical and Mental Health
Introduction:
Thyroid imbalance is a condition that affects the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ situated in the neck. This gland plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism and maintaining the body’s balance. The delicate equilibrium it maintains is crucial for overall health and well-being. When this balance is disrupted, it can give rise to a spectrum of health issues, influencing not just the thyroid but also impacting various systems throughout the body.
Regular monitoring of thyroid function is essential to identify and address potential imbalances. Thyroid Test Packages provide a comprehensive assessment of thyroid hormone levels. These tests are instrumental in the early detection and management of thyroid disorders, allowing individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining their health. Incorporating thyroid tests into routine health assessments, such as master health checkups, can offer a holistic view of one’s well-being.
The Thyroid and Its Functions:
Before delving into the impact of thyroid imbalance, it’s essential to understand the thyroid’s primary functions. The thyroid gland produces hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which play a central role in regulating metabolism. These hormones influence energy production, body temperature, and the function of various organs, ensuring the body’s overall equilibrium.
Common Thyroid Disorders:
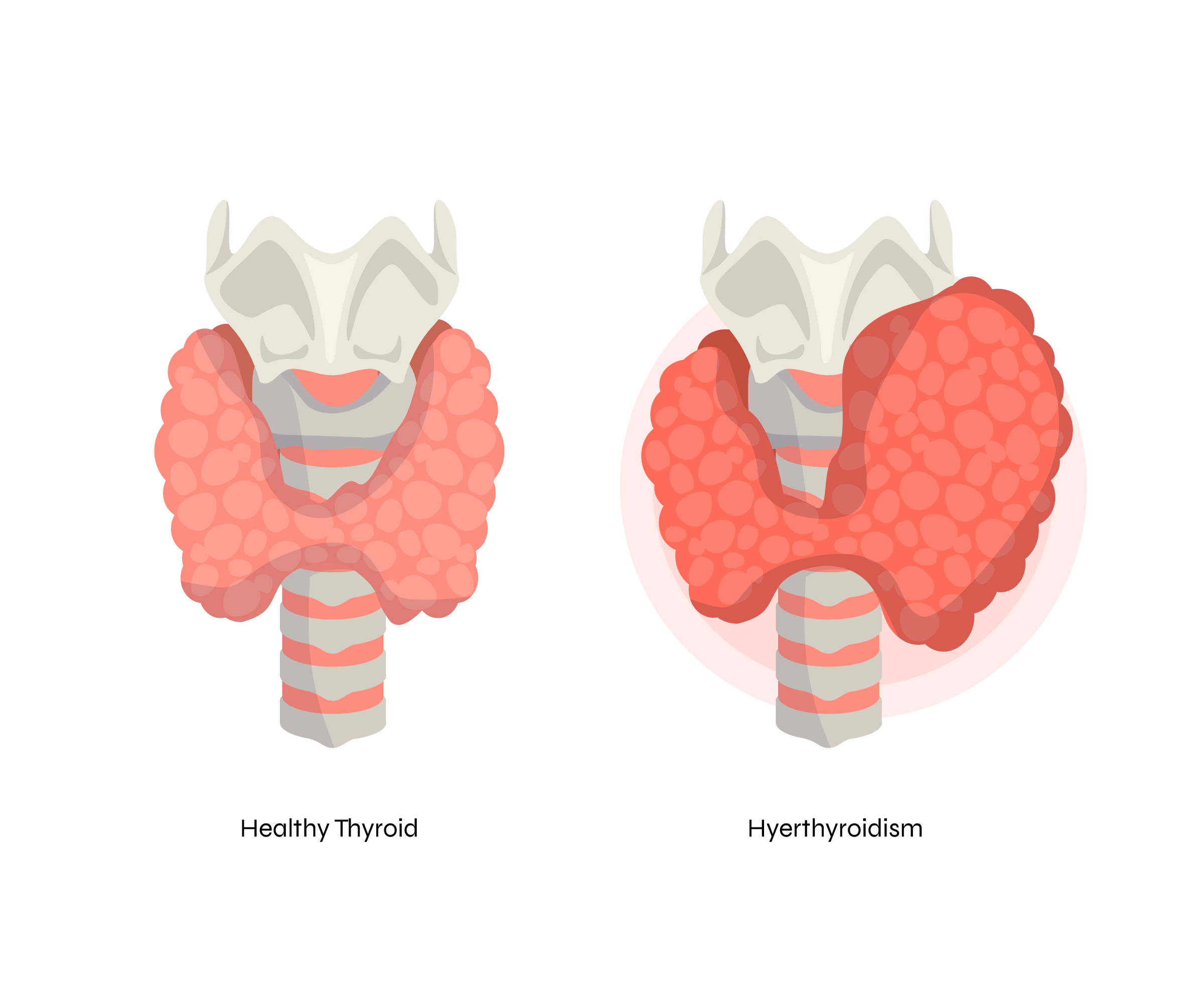
Thyroid imbalance manifests in various forms, with the two most prevalent conditions being hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces insufficient hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism results from an overactive thyroid, causing symptoms like weight loss, anxiety, and increased heart rate.
Impact on Metabolism and Energy Levels:
The thyroid hormones T3 and T4 play a pivotal role in regulating the body’s metabolism. In hypothyroidism, the decreased production of these hormones can slow down metabolism, leading to weight gain, fatigue, and a feeling of constant lethargy. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can accelerate metabolism, causing unintended weight loss, restlessness, and an excess of energy.
Cardiovascular Effects:
Thyroid imbalance can significantly impact the cardiovascular system. Hypothyroidism is associated with elevated cholesterol levels, which can contribute to an increased risk of heart disease. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism can lead to elevated heart rates and increased blood pressure, potentially resulting in heart palpitations and an increased risk of arrhythmias.
Mental Health Implications:
The thyroid gland’s influence extends to mental health, and thyroid imbalance has been linked to mood disorders. Hypothyroidism is often associated with symptoms such as depression, cognitive impairment, and difficulty concentrating. Hyperthyroidism, conversely, can cause anxiety, irritability, and insomnia. Addressing thyroid dysfunction is crucial in managing mental health and achieving overall well-being.
Reproductive Health:
Thyroid hormones play a critical role in reproductive health, and thyroid imbalance can have profound effects on fertility and pregnancy. Women with untreated hypothyroidism may experience menstrual irregularities and difficulty conceiving. During pregnancy, thyroid dysfunction can increase the risk of complications, including preterm birth and developmental issues in the fetus.
Impact on Skin, Hair, and Nails:
Thyroid imbalance can affect the health and appearance of the skin, hair, and nails. Dry skin, brittle nails, and hair loss are common symptoms of hypothyroidism, reflecting the slowed metabolic processes in the body. In contrast, hyperthyroidism may lead to excessive sweating, thinning hair, and changes in skin texture.
Neurological Effects:
Thyroid hormones are crucial for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Thyroid imbalance can contribute to neurological symptoms such as headaches, tremors, and in severe cases, neuropathy. Proper thyroid function is essential for maintaining cognitive function and preventing neurological complications.
Diagnostic Challenges:
Diagnosing thyroid imbalance can be challenging due to its varied symptoms, which can overlap with other medical conditions. Blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels, along with imaging studies like ultrasound, are commonly employed to diagnose and assess the severity of thyroid disorders. Regular monitoring is crucial to adjust treatment plans and ensure optimal thyroid function.
Treatment Options:
Management of thyroid imbalance typically involves medication, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Synthetic thyroid hormones are commonly prescribed to replace deficient hormones in hypothyroidism, while medications that reduce hormone production or activity are used to treat hyperthyroidism. Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, can complement medical treatments and support overall thyroid health.
Conclusion:
The impact of thyroid imbalance on health is extensive and multi-faceted, affecting various systems throughout the body. From metabolism and cardiovascular health to mental well-being and reproductive function, the thyroid’s influence is pervasive. Early detection and appropriate management are crucial in mitigating the impact of thyroid disorders and restoring balance to the body. As research advances, a deeper understanding of the intricate connections between thyroid function and overall health will continue to guide effective treatments and interventions.


